The smart switch and plug market continues to evolve rapidly, with new technologies and capabilities emerging regularly. Understanding upcoming trends helps consumers make forward-looking purchasing decisions and allows businesses to anticipate market shifts. This exploration of future developments highlights the most promising innovations and directional changes that will shape the next generation of these fundamental smart home devices.

Enhanced Intelligence and Autonomy
Smart switches and plugs are becoming increasingly self-sufficient decision-makers rather than simple remote-controlled devices.
Predictive Automation
Future devices will anticipate needs rather than merely responding to commands:
Usage Pattern Learning:
- Devices will analyze historical usage to predict future needs
- Automatic schedule creation based on observed behaviors
- Self-adjusting routines that adapt to seasonal changes
- Identification of anomalous patterns that might indicate problems
Contextual Awareness:
- Integration of multiple data sources for smarter decisions
- Weather-responsive automation without explicit programming
- Occupancy prediction rather than just detection
- Activity recognition to infer appropriate device states
Proactive Suggestions:
- Recommendations for energy optimization
- Identification of devices that would benefit from scheduling
- Suggestions for scene creation based on observed usage
- Alerts for unusual consumption patterns before they become problems
AI-Powered Decision Making
Artificial intelligence will transform basic automation into sophisticated reasoning:
Machine Learning Integration:
- On-device processing for privacy and reduced latency
- Continuous improvement of prediction accuracy over time
- Differentiation between temporary changes and new patterns
- Transfer learning from other users’ anonymized patterns
Behavioral Modeling:
- Creation of household-specific usage models
- Distinction between different users’ preferences
- Adaptation to changing household compositions
- Seasonal and event-based behavioral prediction
Anomaly Detection:
- Identification of potential device failures before they occur
- Security monitoring through usage pattern analysis
- Health and wellness insights through subtle usage changes
- Energy waste identification through comparative analysis
Advanced Energy Management
Energy features will expand beyond simple monitoring to active optimization and grid integration.
Intelligent Load Balancing
Smart devices will actively manage electricity consumption:
Peak Usage Avoidance:
- Automatic shifting of non-critical loads to off-peak hours
- Coordinated operation to prevent simultaneous high draws
- Dynamic response to utility price signals
- Gradual power restoration after outages to prevent surge
Circuit-Level Management:
- Prevention of circuit overloads through coordinated control
- Prioritization of essential devices during limited power scenarios
- Automatic load shedding during approaching capacity limits
- Balanced distribution across phases in three-phase systems
Demand Response Integration:
- Direct participation in utility demand response programs
- Automatic reduction during grid stress events
- Compensation tracking for utility program participation
- User-defined priorities for reduction scenarios
Renewable Energy Optimization
Smart devices will enhance the value of solar, wind, and battery systems:
Solar Synchronization:
- Automatic scheduling of high-consumption devices during peak solar production
- Dynamic adjustment based on weather forecasts
- Optimization for self-consumption versus grid export
- Visual feedback about renewable versus grid energy usage
Battery Storage Integration:
- Intelligent charging and discharging based on production and usage forecasts
- Critical device identification for backup power scenarios
- Extended runtime calculations during outages
- Prioritized charging from renewable sources
Microgrid Coordination:
- Participation in neighborhood-level energy sharing
- Community battery coordination
- Peer-to-peer energy trading facilitation
- Resilience during wider grid outages
Carbon-Aware Operation
Environmental impact will become a primary consideration:
Grid Carbon Intensity Response:
- Scheduling based on electricity generation mix
- Automatic shifting to times of cleaner energy
- Carbon impact reporting and goal setting
- Regional differences in optimization strategies
Embodied Carbon Accounting:
- Lifecycle impact tracking from manufacturing through disposal
- Longevity optimization to reduce replacement frequency
- Upgrade paths that minimize waste
- Material selection for reduced environmental impact
Behavioral Nudging:
- Gentle suggestions for more sustainable usage patterns
- Gamification of energy conservation
- Comparative feedback against similar households
- Goal setting and achievement recognition
Enhanced Connectivity and Interoperability
Future devices will communicate more effectively with broader ecosystems.
Matter Standard Adoption
The unified connectivity standard will transform interoperability:
Universal Compatibility:
- Single devices working across all major ecosystems
- Elimination of ecosystem lock-in concerns
- Simplified setup and configuration
- Consistent experience across platforms
Enhanced Reliability:
- Local control prioritization for critical functions
- Reduced cloud dependency for basic operations
- Mesh networking for improved coverage
- Standardized security implementations
Simplified Consumer Experience:
- Elimination of “works with” confusion
- Consistent control methods across brands
- Unified privacy and security expectations
- Streamlined troubleshooting procedures
Thread and Advanced Networking
Next-generation networking will improve reliability and performance:
Low-Power Mesh Networking:
- Extended battery life for portable devices
- Improved coverage through device-to-device communication
- Self-healing networks that reroute around failures
- Reduced WiFi congestion through dedicated networks
Enhanced Range and Reliability:
- Better penetration through walls and obstacles
- More consistent performance in challenging environments
- Reduced interference susceptibility
- Graceful degradation rather than complete failure
Streamlined Connectivity:
- Simplified pairing processes
- Automatic network optimization
- Bandwidth efficiency improvements
- Coexistence strategies with other wireless technologies
Direct Device-to-Device Communication
Devices will increasingly communicate without central coordination:
Peer-to-Peer Coordination:
- Direct communication between related devices
- Reduced latency for time-sensitive operations
- Continued functionality during hub or internet outages
- Simplified setup for basic device relationships
Distributed Intelligence:
- Shared processing across multiple devices
- Collaborative decision-making
- Redundancy for critical functions
- Resource sharing based on available capacity
Proximity-Based Interactions:
- Automatic contextual awareness based on nearby devices
- Temporary associations when devices are co-located
- Location-specific behavior adaptations
- Seamless transitions as users move between spaces
Physical Design Evolution
The form and function of smart switches and plugs will continue to evolve.
Miniaturization and Integration
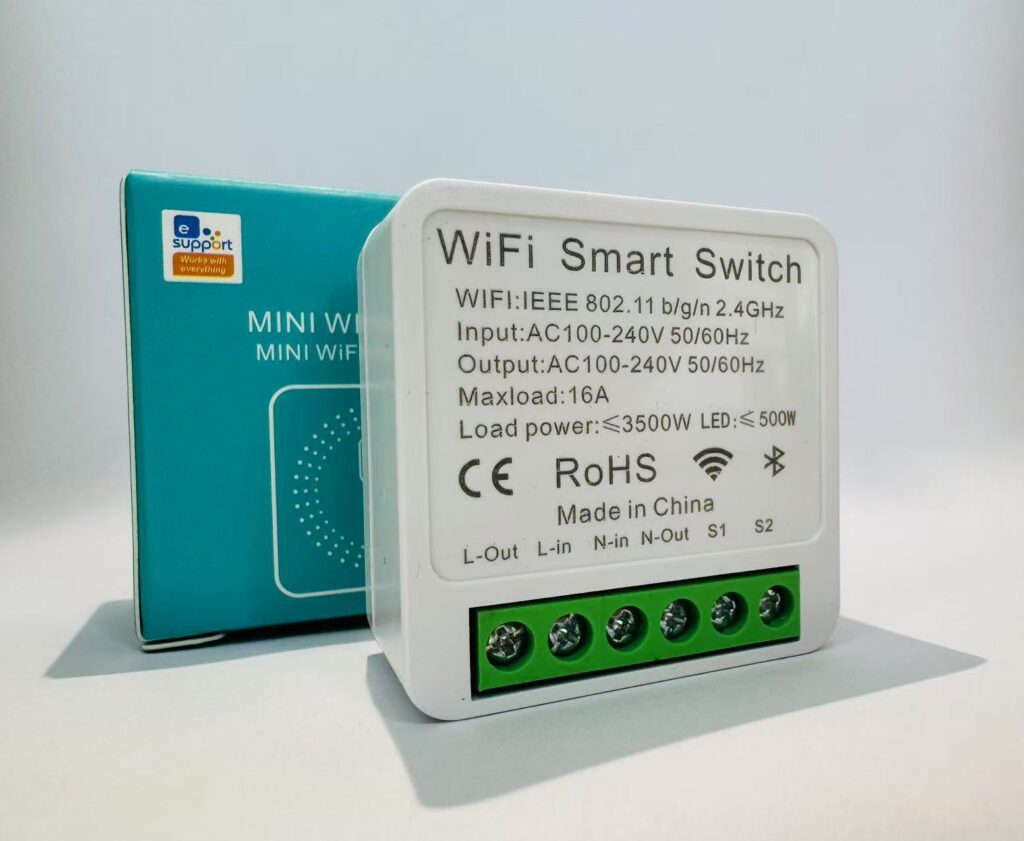

Our best-selling 16A Mini WiFi Smart Switch.
Devices will become less visually intrusive:
Component Size Reduction:
- Smaller profiles that don’t block adjacent outlets
- In-wall modules that fit into standard electrical boxes
- Integrated solutions that replace traditional outlets entirely
- Reduced depth requirements for installation
Invisible Integration:
- Behind-the-scenes installation options
- Flush mounting with no visible protrusion
- Integration directly into appliances and fixtures
- Concealed installation with remote sensors
Modular Approaches:
- Base units with optional feature modules
- Upgradable components to extend lifespan
- Customizable configurations for specific needs
- Standardized form factors across manufacturers
Enhanced User Interfaces
Interaction methods will become more intuitive and informative:
Advanced Visual Feedback:
- Color-changing surfaces to indicate status
- E-ink displays for persistent information
- Ambient light adaptation for optimal visibility
- Projection capabilities for larger information display
Expanded Input Methods:
- Gesture recognition for touchless control
- Pressure sensitivity for contextual responses
- Proximity detection for anticipatory activation
- Multi-touch capabilities for complex interactions
Accessibility Improvements:
- Tactile indicators for visually impaired users
- Auditory feedback options
- Multiple interaction modalities for diverse needs
- Customizable interface sensitivity and response
Sustainable Materials and Design
Environmental considerations will influence physical construction:
Eco-Friendly Materials:
- Biodegradable or recyclable housings
- Reduced plastic content
- Sustainable sourcing certification
- Non-toxic component selection
Repairability Focus:
- Modular design for component replacement
- User-serviceable parts where safety permits
- Extended support lifecycles
- Documented repair procedures
Energy-Efficient Components:
- Lower standby power consumption
- More efficient wireless communications
- Optimized power supply design
- Energy harvesting for supplemental power
Enhanced Security and Privacy
Protection of data and systems will become increasingly sophisticated.
Robust Device Security
Protection against exploitation will improve significantly:
Hardware Security Modules:
- Dedicated security chips for credential protection
- Physical tampering detection
- Secure boot processes
- Cryptographic acceleration for better performance
Zero-Trust Architectures:
- Continuous verification rather than one-time authentication
- Least-privilege operation by default
- Segmentation of critical functions
- Regular security posture reassessment
Automated Security Maintenance:
- Seamless security updates without user intervention
- Vulnerability scanning and remediation
- Certificate rotation and management
- Proactive threat monitoring and response
Privacy-Preserving Technologies
User data protection will become a primary design consideration:
Local Processing Priority:
- On-device analysis of sensitive data
- Minimized cloud transmission
- Edge computing for privacy-sensitive functions
- User control over data sharing granularity
Transparent Data Practices:
- Clear communication about data collection
- Easily accessible privacy controls
- Retention limitations by design
- Purpose limitation enforcement
Anonymization Techniques:
- Differential privacy implementations
- Aggregated rather than individual data sharing
- Pseudonymization of necessary identifiers
- Data minimization by default
Resilience Against Disruption
Systems will maintain functionality during challenging conditions:
Offline Capabilities:
- Core functions operating without internet connectivity
- Local storage of essential automation rules
- Graceful degradation during service interruptions
- Transparent communication about offline limitations
Backup Power Options:
- Battery backup for critical functions
- Low-power operating modes during outages
- Prioritized restoration of essential services
- Clear indication of backup status and runtime
Disaster Recovery:
- Automated configuration backups
- Quick restoration procedures
- Alternative control methods during primary system failure
- Resilient design for environmental challenges
Specialized Applications and Markets
Smart switches and plugs will evolve to address specific use cases and environments.
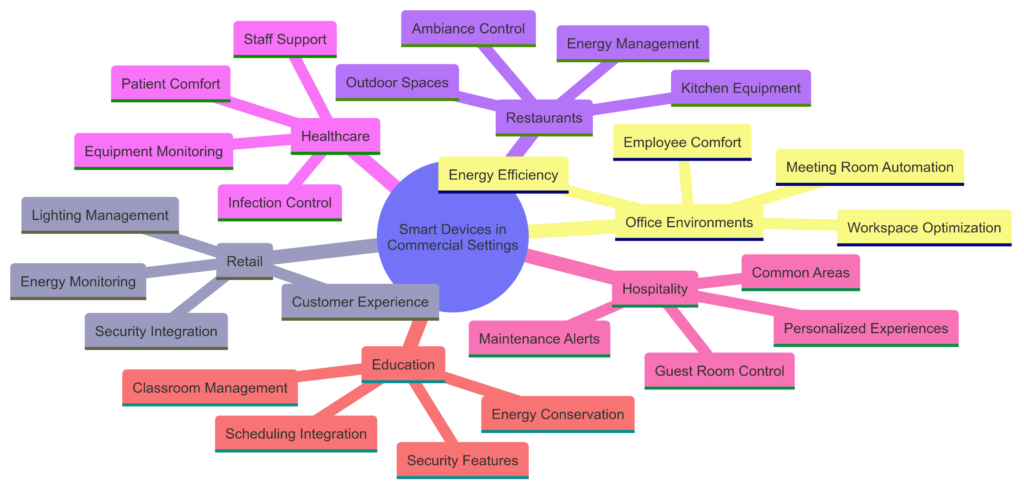
Commercial Application Scenarios
Commercial and Industrial Adaptations
Business-focused versions will offer enhanced capabilities:
Enterprise Management:
- Centralized deployment and configuration
- Role-based access control
- Integration with building management systems
- Detailed audit logging and compliance features
High-Reliability Designs:
- Redundant components for critical applications
- Industrial temperature ratings
- Enhanced surge and electrical noise immunity
- Continuous duty cycle ratings
Specialized Certifications:
- Healthcare environment compliance
- Educational institution safety features
- Hospitality-specific capabilities
- Retail environment optimizations
Health and Wellness Applications
Smart devices will increasingly support wellbeing:
Circadian Rhythm Support:
- Automatic color temperature and brightness adjustment
- Sleep cycle-aware operation
- Seasonal affective disorder countermeasures
- Personalized lighting preferences by user
Air Quality Management:
- Coordinated control of purification devices
- Ventilation optimization based on pollutant levels
- Humidity control for health and comfort
- Allergen reduction strategies
Aging-in-Place Support:
- Unusual pattern detection for wellness checks
- Medication reminder integration
- Simplified interfaces for accessibility
- Emergency response system integration
Specialized Environmental Applications
Devices designed for challenging locations:
Extreme Weather Resilience:
- Extended temperature operating ranges
- Humidity and moisture resistance
- UV and corrosion protection
- Impact and vibration resistance
Agricultural Adaptations:
- Dust and particulate protection
- Chemical exposure resistance
- Integration with irrigation and climate control
- Remote deployment considerations
Marine and Coastal Versions:
- Saltwater corrosion resistance
- Waterproof designs beyond typical ratings
- Anti-fouling properties
- Integration with marine electrical systems
The future of smart switches and plugs will be characterized by greater intelligence, improved energy management, enhanced connectivity, evolved physical design, stronger security, and specialized applications. These devices will transition from simple remote-controlled products to sophisticated nodes in an intelligent network, making increasingly autonomous decisions while providing users with greater insight and control when desired. By understanding these emerging trends, consumers and businesses can make forward-looking decisions that maximize long-term value and compatibility with the evolving smart home ecosystem.
